NPK, the three essential nutrients – Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) – is critical for plant growth and development. Each element serves a unique purpose and contributes to different aspects of plant health. Understanding how to use NPK for plants can significantly enhance your gardening or farming efforts.
Understanding NPK: The Basics
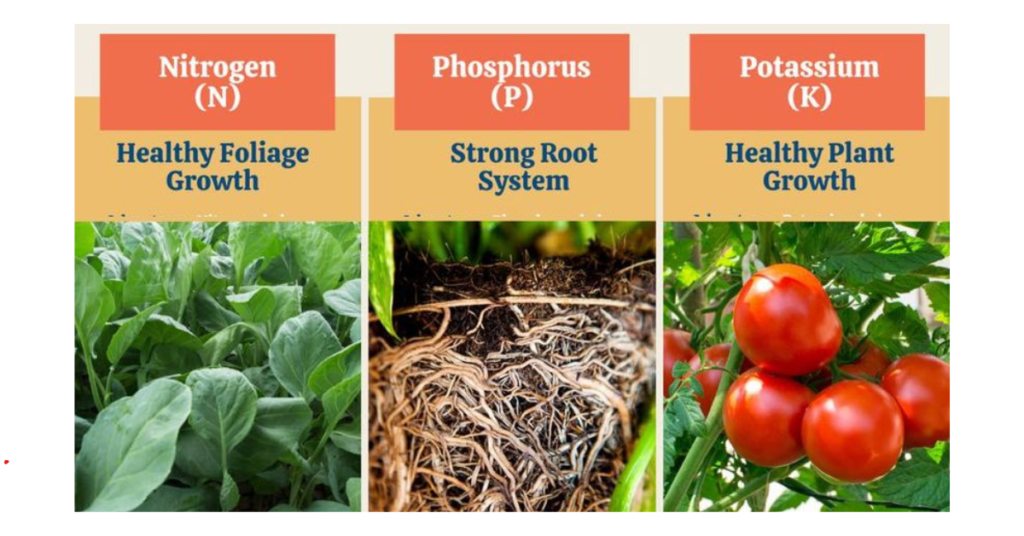
NPK stands for Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K), the primary macronutrients required by plants. These nutrients are often found in fertilizers and are crucial for various physiological functions. Nitrogen is vital for leaf and stem growth, phosphorus aids in root development and flowering, and potassium ensures overall plant health and disease resistance.
Importance of Nitrogen in Plant Growth
Nitrogen is a key component of chlorophyll, the compound responsible for photosynthesis. It helps plants convert sunlight into energy. Adequate nitrogen ensures lush, green foliage and promotes vigorous growth. However, too much nitrogen can lead to excessive leaf growth at the expense of fruits and flowers.
Role of Phosphorus in Plants
Phosphorus is essential for energy transfer within plants. It plays a critical role in photosynthesis, respiration, and energy storage. Phosphorus promotes strong root development and boosts the plant’s ability to flower and set seeds. Deficiency in phosphorus can result in stunted growth and poor flowering.
Benefits of Potassium for Plants
Potassium is crucial for the overall health and vigor of plants. It regulates water uptake and loss, ensuring that plants maintain proper hydration. Potassium also strengthens plant tissues, making them more resistant to diseases and pests. Additionally, it aids in the synthesis of proteins and starches.
How to Use NPK for Plants: {Soil Testing}
Before applying NPK fertilizers, it’s essential to conduct a soil test. Soil testing helps determine the existing nutrient levels and pH balance of your soil. This information is critical to deciding the right type and amount of NPK fertilizer needed. Over-fertilizing can lead to nutrient imbalances and environmental issues.
Choosing the Right NPK Ratio

Different plants have varying nutrient requirements. Understanding how to use NPK for plants involves selecting the correct NPK ratio for your specific crops. For example, leafy vegetables like lettuce may require a higher nitrogen ratio, while flowering plants like tomatoes benefit from a balanced or slightly higher phosphorus content.
Application Methods for NPK Fertilizers
NPK fertilizers can be applied in various ways, including broadcasting, side-dressing, and foliar feeding. Broadcasting involves spreading the fertilizer evenly across the soil surface. Side-dressing places the fertilizer in a band along the sides of plants, and foliar feeding involves spraying a diluted fertilizer solution directly onto the leaves.
Timing and Frequency of NPK Application
Knowing when and how often to apply NPK fertilizers is crucial. Generally, the best time to fertilize is during the growing season when plants are actively developing. Depending on the type of plants and soil conditions, you may need to apply fertilizers every few weeks or less frequently.
Organic vs. Synthetic NPK Fertilizers
There are both organic and synthetic NPK fertilizers available. Organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, release nutrients slowly and improve soil health over time. Synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability but can lead to soil degradation if used excessively. Choosing between them depends on your gardening philosophy and specific needs.
Common Signs of NPK Deficiency
Recognizing the signs of NPK deficiency is essential for timely intervention. Nitrogen deficiency often manifests as yellowing leaves and stunted growth. Phosphorus deficiency can cause dark, bluish-green foliage and poor root development. Potassium deficiency typically shows as browning and curling leaf edges.
Avoiding Over-Fertilization
Over-fertilization can be as detrimental as nutrient deficiency. It can lead to nutrient runoff, pollution, and plant damage. Symptoms of over-fertilization include leaf burn, weak growth, and imbalanced nutrient uptake. Always follow recommended guidelines and adjust based on plant response and soil tests.
Conclusion
Understanding how to use NPK for plants is fundamental for achieving optimal plant health and productivity. By carefully selecting the right NPK ratio, applying it correctly, and monitoring plant responses, gardeners and farmers can ensure their plants receive the nutrients they need.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the best NPK ratio for tomatoes?
The best NPK ratio for tomatoes is typically 5-10-10 or 10-10-10, emphasizing phosphorus for strong root and flower development.
2. How often should I apply NPK fertilizer to my garden?
It depends on the plants and soil conditions. Generally, applying every 4-6 weeks during the growing season is effective.
3. Can I use NPK fertilizer on indoor plants?
Yes, but it’s crucial to use a diluted solution and follow the specific nutrient needs of each indoor plant species.
4. What happens if I use too much NPK fertilizer?
Overuse can lead to nutrient imbalances, plant damage, and environmental issues such as water pollution.
5. How can I tell if my soil needs more nitrogen?
Signs of nitrogen deficiency include yellowing leaves, particularly older ones, and stunted plant growth. Conduct a soil test for accurate assessment.