Introduction:
NPK fertilizers are the cornerstone of plant nutrition, providing essential nutrients for healthy growth and development. Understanding the role of NPK – nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium – is crucial for optimizing plant health and productivity. In this article, we delve into the uses of NPK for plants, exploring how each nutrient contributes to overall growth and vitality.

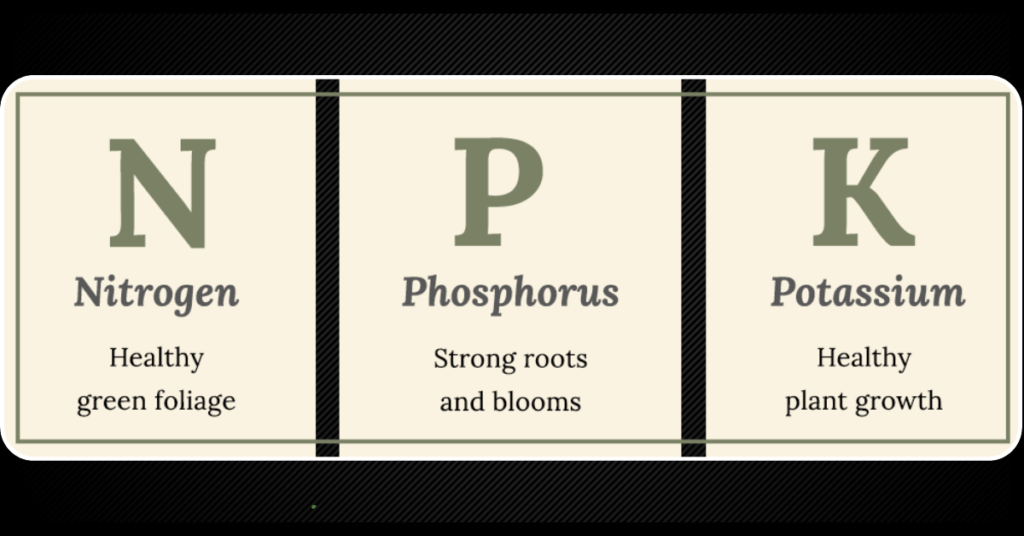
1. Nitrogen: Fueling Lush Greenery
Nitrogen, often represented by the first number in fertilizer labels, is vital for plant growth. It plays a central role in the synthesis of chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for photosynthesis. Adequate nitrogen levels result in lush, green foliage, making it essential for leafy vegetables, lawns, and other green plants. Without sufficient nitrogen, plants may exhibit stunted growth and yellowing leaves, indicating nutrient deficiency.
2. Phosphorus: Stimulating Root Development
Phosphorus, denoted by the second number in fertilizer formulations, is crucial for root development and overall plant energy transfer. It aids in the formation of essential molecules like ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which powers various cellular processes. Phosphorus promotes robust root growth, enhancing nutrient uptake and water absorption. It is particularly important during the early stages of plant growth and flowering, facilitating strong root systems and vibrant blooms.
3. Potassium: Enhancing Stress Tolerance
Potassium, represented by the third number in NPK fertilizers, plays a multifaceted role in plant physiology. It regulates water movement, enzyme activation, and photosynthesis, contributing to overall stress tolerance and disease resistance. Adequate potassium levels bolster plant resilience against environmental stressors such as drought, pests, and diseases. Additionally, potassium promotes fruit development and quality, making it indispensable for crop production and overall yield.
4. Balanced NPK: Achieving Optimal Growth
Achieving a balanced NPK ratio is essential for promoting optimal plant growth and health. Different plants have varying nutrient requirements at different growth stages, necessitating tailored fertilizer formulations. Soil testing can help determine existing nutrient levels and guide fertilizer application rates to address specific deficiencies. By providing the right balance of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, plants can thrive, exhibiting vigorous growth, abundant blooms, and bountiful harvests.
5. Customizing NPK Fertilizations
Customizing NPK fertilization involves understanding the unique requirements of different plant species and growth stages. Some plants, such as leafy greens and grasses, benefit from higher nitrogen levels to support foliage development. Others, like flowering plants and fruit-bearing trees, require increased phosphorus and potassium for flowering, fruit set, and overall reproductive success. By adjusting NPK ratios based on plant needs, gardeners and farmers can maximize productivity while minimizing nutrient waste.
6. Organic vs. Synthetic NPK Fertilizers:
When choosing NPK fertilizers, gardeners often face the choice between organic and synthetic formulations. Organic fertilizers, derived from natural sources like compost, bone meal, and seaweed, provide slow-release nutrients and improve soil structure over time. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, offer precise nutrient concentrations and immediate plant uptake but may contribute to soil degradation and environmental pollution if overused. Understanding the pros and cons of each type can help make informed decisions regarding NPK fertilizer selection.
7. Sustainable NPK Practices: Balancing Productivity and Environmental Impact
Incorporating sustainable NPK practices involves optimizing nutrient use efficiency while minimizing environmental harm. This can be achieved through practices such as precision agriculture, cover cropping, and nutrient recycling. By applying NPK fertilizers judiciously, minimizing runoff, and adopting soil conservation techniques, growers can enhance crop yields while safeguarding soil health and water quality for future generations.
8. NPK for Indoor Plants
Indoor plants, confined to containers or indoor environments, rely solely on provided nutrients for growth. NPK fertilization is crucial for replenishing essential nutrients depleted from potting mixes over time. Choosing a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for indoor plants can help meet their unique nutrient demands, promoting healthy growth and vibrant foliage year-round.
9. Common NPK Fertilizer Mistakes: Avoiding Pitfalls
Despite its benefits, improper NPK fertilizer application can lead to nutrient imbalances, soil acidity, and environmental pollution. Common mistakes include over-fertilization, neglecting soil testing, and applying fertilizers at the wrong time or in unfavorable conditions. By following recommended guidelines, monitoring plant responses, and adjusting fertilization practices as needed, growers can avoid these pitfalls and promote sustainable plant nutrition.
10. Conclusion
In conclusion, NPK fertilizers are indispensable tools for promoting plant health, productivity, and resilience. Understanding the unique roles of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium allows growers to tailor fertilization practices to meet specific plant needs and growth stages. By adopting sustainable fertilization practices and avoiding common pitfalls, gardeners and farmers can harness the power of NPK to cultivate thriving gardens, lush landscapes, and abundant harvests.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the primary uses of NPK for plants?
NPK fertilizers provide essential nutrients – nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium – vital for plant growth, development, and overall health. They promote lush foliage, robust root systems, flower formation, and fruit development.
2. How do I determine the right NPK ratio for my plants?
The ideal NPK ratio varies depending on plant species, growth stage, and soil conditions. Conducting soil tests can help identify existing nutrient levels and guide fertilizer selection and application rates to address specific deficiencies.
3. Can I use NPK fertilizers for all types of plants?
While NPK fertilizers are beneficial for most plants, it’s essential to consider individual plant requirements and adjust nutrient ratios accordingly. Some plants may have specific nutrient needs or be sensitive to certain fertilizer formulations.
4. What is the difference between organic and synthetic NPK fertilizers?
Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources and provide slow-release nutrients, improving soil structure over time. Synthetic fertilizers offer precise nutrient concentrations for immediate plant uptake but may contribute to environmental pollution if overused.
5. How often should I apply NPK fertilizers to my plants?
The frequency of NPK fertilizer application depends on factors such as plant type, growth stage, soil fertility, and environmental conditions. It’s essential to follow recommended guidelines and monitor plant responses to avoid over-fertilization or nutrient deficiencies.