Introduction
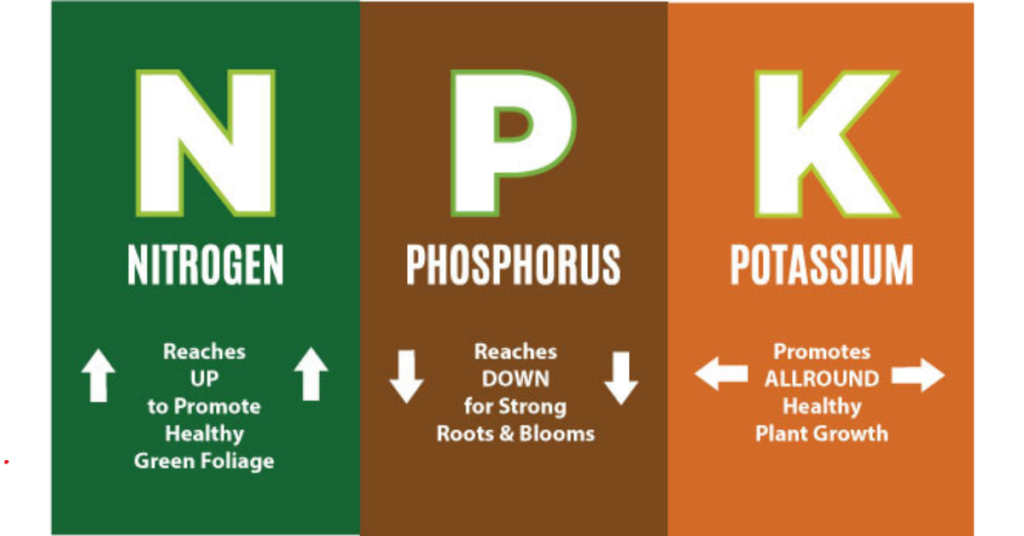
In the world of gardening and agriculture, the acronym NPK stands for Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K). These three elements are the primary nutrients essential for plant growth and development. Each of these nutrients plays a unique and crucial role in the health and productivity of plants. Understanding what NPK does for plants can significantly improve your gardening or farming results, ensuring lush, healthy plants and bountiful harvests.
The Role of Nitrogen in Plant Growth
Nitrogen is a vital component of chlorophyll, the compound that plants use in photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy. This nutrient is also a fundamental part of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, which are necessary for the growth and development of plant tissues. Adequate nitrogen levels lead to vigorous growth, healthy leaves, and robust stems. Without sufficient nitrogen, plants can exhibit stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and overall poor health.
The Importance of Phosphorus in Plants
Phosphorus is crucial for energy transfer and storage within the plant. It is a key component of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is essential for energy transfer during photosynthesis and respiration. Phosphorus also plays a significant role in root development, flowering, and fruiting. Plants that receive enough phosphorus have strong roots, better resistance to disease, and improved flowering and fruit production. A deficiency in phosphorus can lead to weak root systems, delayed growth, and poor seed and fruit quality.
The Potassium Factor in Plant Health
Potassium is an essential nutrient that helps regulate various physiological processes in plants, including water uptake and enzyme activation. It is vital for photosynthesis, protein synthesis, and overall plant metabolism. Potassium also enhances drought resistance, strengthens cell walls, and improves the plant’s ability to resist diseases. A lack of potassium can result in weak stems, poorly developed roots, and leaves with brown edges or spots.
Balancing NPK Ratios for Optimal Growth

The right balance of NPK in the soil is crucial for the optimal growth of plants. Different plants have varying nutrient requirements, and the ideal NPK ratio can depend on the specific plant species, soil type, and growth stage. For example, leafy vegetables typically require higher nitrogen levels, while flowering and fruiting plants benefit from increased phosphorus and potassium. Soil testing is an effective way to determine the existing nutrient levels and adjust fertilization practices accordingly.
The Effects of NPK on Soil Health
NPK fertilizers not only provide essential nutrients to plants but also influence soil health. Overuse of nitrogen can lead to soil acidification, while excessive phosphorus can cause nutrient imbalances and environmental pollution due to runoff. It is essential to apply NPK fertilizers judiciously, considering both plant needs and soil health. Organic matter, crop rotation, and the use of cover crops can help maintain soil fertility and structure alongside NPK fertilization.
Organic vs. Synthetic NPK Fertilizers
NPK fertilizers are available in both organic and synthetic forms. Organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, release nutrients slowly and improve soil structure and microbial activity. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, provide immediate nutrient availability but may not enhance soil health in the long term. Each type has its advantages and limitations, and choosing the right one depends on your specific gardening goals and soil conditions.
Symptoms of NPK Deficiencies in Plants
Recognizing the symptoms of NPK deficiencies can help in timely intervention and correction. Nitrogen deficiency often results in yellowing leaves and stunted growth. Phosphorus deficiency may cause dark green or purplish foliage and poor root development. Potassium deficiency is typically indicated by browning and curling leaf edges. Regular monitoring and soil testing can help identify and address these deficiencies effectively.
How to Apply NPK Fertilizers Correctly
Applying NPK fertilizers correctly ensures that plants receive the maximum benefit without causing harm to the soil or environment. It is crucial to follow recommended application rates and timings based on soil tests and plant needs. Over-fertilization can lead to nutrient runoff and environmental pollution, while under-fertilization can result in poor plant growth. Techniques such as side-dressing, foliar feeding, and slow-release fertilizers can be employed for efficient nutrient delivery.
Environmental Impact of NPK Fertilizers
While NPK fertilizers are essential for plant growth, their use must be managed to minimize environmental impact. Excessive use of nitrogen and phosphorus can lead to water pollution, causing eutrophication in water bodies and harming aquatic life. Sustainable fertilization practices, including precision farming, controlled-release fertilizers, and integrated nutrient management, can help reduce the environmental footprint of NPK fertilizers.
Innovations in NPK Fertilization
Recent advancements in agricultural technology have led to the development of more efficient and sustainable NPK fertilization methods. Innovations such as soil sensors, precision agriculture tools, and customized nutrient formulations are helping farmers optimize fertilizer use, improve crop yields, and minimize environmental impact. These technologies represent the future of fertilization, ensuring food security while protecting natural resources.
Conclusion
Understanding what NPK does for plants is fundamental for successful gardening and farming. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium each play vital roles in plant growth and development. By carefully managing the application of NPK fertilizers, gardeners and farmers can promote healthy plant growth, improve soil health, and protect the environment. Balancing these nutrients, recognizing deficiency symptoms, and adopting sustainable fertilization practices are key to achieving optimal plant health and productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does NPK stand for?
NPK stands for Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K), the three primary nutrients essential for plant growth.
2. How does nitrogen affect plant growth?
Nitrogen is crucial for chlorophyll production and protein synthesis, leading to vigorous growth and healthy leaves.
3. Why is phosphorus important for plants?
Phosphorus is vital for energy transfer, root development, and flowering, improving overall plant health and productivity.
4. What are the signs of potassium deficiency in plants?
Potassium deficiency can cause browning and curling of leaf edges, weak stems, and poorly developed roots.
5. Can I use organic NPK fertilizers?
Yes, organic NPK fertilizers such as compost and manure provide essential nutrients and improve soil health over time.