Introduction to NPK for Plants
In the realm of gardening and agriculture, understanding the nutritional needs of plants is fundamental for healthy growth. One critical aspect of plant nutrition revolves around the acronym “NPK,” which stands for nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). These three key nutrients are essential for the growth, development, and overall health of plants. This blog post will delve into what NPK for plants really means, its importance, and how to manage it effectively.
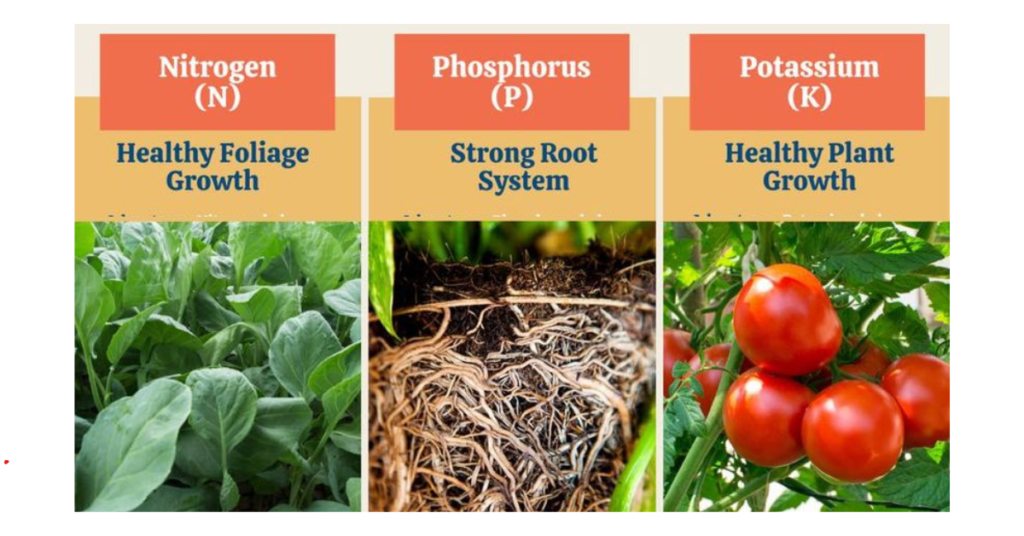
The Role of Nitrogen (N) in Plant Growth
Nitrogen is vital for plant growth as it’s a major component of chlorophyll, the compound plants use to photosynthesize and produce energy. It also plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, affecting the plant’s overall growth and vitality. Adequate nitrogen ensures lush, vibrant foliage and supports rapid growth.
Phosphorus (P): Enhancing Energy and Root Development
Phosphorus is key to the formation of DNA and RNA, which are essential for cell division and development in plants. It helps in energy transfer within the plant, promoting healthy root development and blooming. Understanding what NPK for plants entails, phosphorus stands out as a growth initiator, especially in the early stages of a plant’s life cycle.
Potassium (K): The Regulator of Plant Functions
Potassium regulates various plant functions, including water uptake, enzyme activation, and photosynthesis. It helps strengthen plants’ resistance to diseases and environmental stresses like drought and frost. Potassium ensures that plants remain healthy and robust, contributing to their structural integrity and physiological processes.
Balancing NPK Ratios for Optimal Plant Health
The balance of NPK in fertilizer affects plant health significantly. Each plant species and its growth stage require specific NPK ratios for optimal development. Gardeners and farmers must adjust these ratios according to the plant’s current needs, which vary from the growth phase to the flowering or fruit-bearing stages.
Significance of NPK in Soil Fertility
Soil fertility largely depends on the presence and balance of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Regular soil testing can reveal which nutrients are deficient and guide the appropriate fertilizer application, ensuring that plants receive the right nutrition at the right time.
NPK and Water Solubility: Absorption Efficiency
The water solubility of NPK fertilizers affects their efficiency and the speed at which plants can absorb these nutrients. Soluble fertilizers provide immediate nutritional benefits to plants, especially crucial during critical growth phases where nutrient demands are higher.
Organic vs. Synthetic NPK Fertilizers
The choice between organic and synthetic NPK fertilizers can influence plant health and environmental impact. Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly and improve soil structure, while synthetic fertilizers offer quick nutrient release but can lead to nutrient runoff and environmental degradation.
Impact of Over-Fertilization
While it’s essential to understand what NPK for plants is, it’s equally important to avoid over-fertilization. Excess nutrients can lead to nutrient burn, where plants display scorched tips and stunted growth, and can adversely affect soil health and microbial balance.
Adapting NPK Usage to Specific Plant Needs
Each plant type has unique nutritional needs, and tailoring NPK applications to these needs can lead to healthier, more productive plants. For instance, leafy greens may require higher nitrogen levels, whereas flowering plants might benefit more from increased phosphorus.
Seasonal Variations in NPK Requirements
Seasonal changes affect plant nutrient requirements. Spring might call for higher nitrogen levels to support growth, while phosphorus and potassium are more crucial in the fall to help plants prepare for winter.
Conclusion: The Essentials of NPK for Plants
Understanding what NPK for plants entails is crucial for anyone involved in plant care and agriculture. Proper management of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium not only supports plant health but also enhances yield and the aesthetic quality of gardens and crops. By mastering NPK application, gardeners and farmers can ensure that their plants thrive in various conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About NPK for Plants
1. What does NPK stand for in gardening?
NPK stands for nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), which are the three primary nutrients required for healthy plant growth.
2. How do I know if my soil is deficient in NPK?
Soil testing is the most accurate way to determine nutrient deficiencies in your soil. This test will help you understand if you need to adjust your fertilizer application.
3. Can I use the same NPK ratio for all types of plants?
No, different plants require different NPK ratios depending on their specific growth needs and stages. Tailoring your fertilizer application to each plant type is essential for optimal growth.
4. What are the signs of NPK deficiency in plants?
Signs of NPK deficiency include yellowing leaves (nitrogen deficiency), stunted growth and dark green leaves (phosphorus deficiency), and scorched leaf edges and weak stems (potassium deficiency).
5. Where can I buy NPK fertilizers?
NPK fertilizers are available at garden centers, home improvement stores, and online retailers. Be sure to choose a product that suits your specific gardening needs.